Are you struggling to choose between belt-drive and direct-drive air compressors? Each has its strengths, but which suits you best?
The right compressor can impact energy efficiency, cost, and long-term performance. Belt-driven models offer flexibility and affordability, while direct-drive systems excel in durability and energy savings.
In this post, you’ll learn the differences, advantages, and ideal uses for both types. We’ll compare factors like cost, maintenance, and efficiency to help you make the best choice for your needs.

What is a Direct Drive Air Compressor?
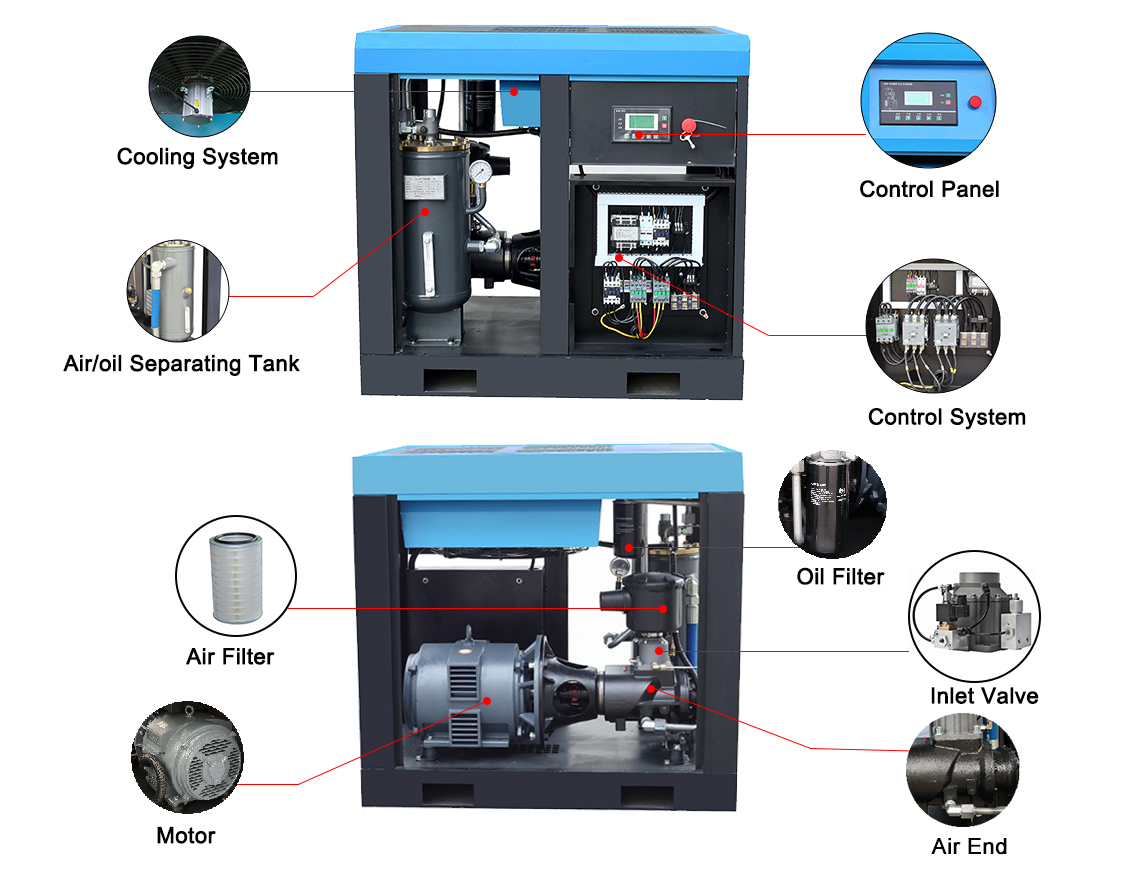
A direct drive air compressor, also known as a coupled compressor, is a type of compressor where the crankshaft is directly connected to the motor without using belts or pulleys. This design eliminates the need for intermediate components, resulting in a more compact and efficient system.
Key Components
The main components of a direct drive air compressor include:
Motor: Powers the compressor and directly drives the crankshaft.
Crankshaft: Converts the rotary motion of the motor into the reciprocating motion needed by the pistons.
Compressor Pump: Contains the pistons, valves, and cylinders that compress the air.
Best Seller 110KW 150HP Direct Drive Rotary Air Compressor For Railway Head Project
How It Works
In a direct drive system, the motor's rotation is directly transferred to the crankshaft, which in turn drives the compressor pump. As the crankshaft rotates, it moves the pistons inside the cylinders, drawing in air through the inlet valves and compressing it. The compressed air is then discharged through the outlet valves into the storage tank or directly to the pneumatic tools.
Advantages of Direct Drive Compressors
Energy Efficiency: With fewer moving parts and no power loss through belts or pulleys, direct drive compressors are more energy-efficient than their belt-driven counterparts.
Low Maintenance: The simple design of direct drive compressors results in fewer components that can wear out or require replacement, reducing maintenance requirements and costs.
Durability in Harsh Environments: Direct drive compressors can withstand extreme temperatures and harsh operating conditions, making them suitable for outdoor and industrial applications.
Ideal for Heavy-Duty Use: The robust construction and efficient power transfer make direct drive compressors well-suited for constant, heavy-duty industrial use.
Disadvantages of Direct Drive Compressors
Limited Pressure and Speed Adjustment: Unlike belt-driven compressors, direct drive models offer little flexibility in adjusting the pressure or speed without changing the motor or gearing.
Higher Repair Costs: If a component fails, repairs can be more expensive and complex due to the direct connection between the motor and compressor pump.
Increased Noise Levels: Direct drive compressors tend to produce more noise than belt-driven models because the motor and pump are directly coupled, transmitting more vibrations.
Higher Initial Cost: Due to their heavy-duty construction and more sophisticated components, direct drive compressors often have a higher upfront cost compared to belt-driven models.
What is a Belt Driven Air Compressor?
A belt driven air compressor is a type of compressor that uses a belt and pulley system to connect the motor to the compressor pump. This system allows for power transmission from the motor to the pump, enabling the compression of air.
Key Components
The main components of a belt driven air compressor include:
Motor: Provides the power to drive the compressor pump.
Pulley System: Consists of two or more pulleys that are connected by a belt.
Belt: Transfers power from the motor pulley to the compressor pump pulley.
Compressor Pump: Contains the pistons, valves, and cylinders responsible for compressing the air.

Silent Oilless Oil Free Belt Driven Scroll Air Compressor for Sal
How Belt Drive Systems Work
In a belt driven air compressor, the motor rotates a pulley that is connected to the compressor pump pulley via a belt. As the motor runs, it turns the belt, which in turn rotates the compressor pump. The pump then draws in air, compresses it, and sends it to the storage tank or directly to the pneumatic tools.
Advantages of Belt Driven Air Compressors
Flexibility: Belt driven compressors offer a high degree of flexibility in terms of pressure adjustment. By changing the size of the pulleys, you can easily modify the pressure output to suit your specific needs.
Quiet Operation: When properly lubricated, belt driven compressors tend to run more quietly and smoothly than direct drive models. This makes them ideal for use in indoor environments or areas where noise levels need to be kept to a minimum.
Easy Maintenance: Maintaining a belt driven compressor is relatively simple and economical. Regular tasks include checking belt tension, aligning pulleys, and replacing worn belts as needed.
Lower Initial Cost: Compared to direct drive compressors, belt driven models generally have a lower upfront cost, making them a more budget-friendly option for those with limited financial resources.
Suitable for Intermittent Use: Belt driven compressors are well-suited for applications that require intermittent or light-duty use, such as in small workshops or for hobbyists.
Disadvantages of Belt Driven Air Compressors
Belt Wear and Tear: Over time, the belts in a belt driven compressor can stretch, wear out, or even break, requiring regular replacement to maintain optimal performance.
Regular Maintenance: To ensure proper operation and longevity, belt driven compressors require regular tensioning and alignment checks. Failure to perform these tasks can lead to decreased efficiency and potential damage to the compressor.
Temperature Sensitivity: Belt driven compressors are more sensitive to extreme temperatures than direct drive models. Very high or low temperatures can cause the belts to deteriorate more quickly, leading to premature failure.
Slightly Lower Efficiency: Due to the power loss through the belt and pulley system, belt driven compressors are slightly less energy-efficient than their direct drive counterparts.
The Differences Between Belt Drive and Direct Drive
While both belt drive and direct drive air compressors serve the purpose of compressing air, they have several distinct differences. Understanding these differences is crucial in determining which type of compressor is best suited for your specific needs.
| Feature |
Belt Drive |
Direct Drive |
| Efficiency |
Lower (power loss due to belts) |
Higher (fewer moving parts) |
| Power Output |
Higher (increased torque) |
Lower |
| Maintenance Needs |
Higher (belt replacements) |
Lower |
| Noise Levels |
Lower (belts absorb vibrations) |
Higher (direct vibration transfer) |
| Initial Cost |
Lower |
Higher |
| Lifetime Cost |
Higher (maintenance, efficiency) |
Lower (efficiency, less maintenance) |
| Environmental Tolerance |
Lower (sensitive to temperature) |
Higher (withstands extremes) |
| Flexibility |
Higher (adjustable pulleys) |
Lower (limited adjustments) |
| Applications |
Light-duty, intermittent use |
Heavy-duty, continuous use |
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Belt Drive vs Direct Drive
When deciding between a belt drive and direct drive air compressor, it's essential to consider several key factors that will impact the performance, efficiency, and longevity of your compressor. Take into account your usage patterns, budget, energy efficiency, maintenance capabilities, operating environment, and flexibility requirements to make an informed decision.
Usage Patterns
Your usage patterns, including the frequency and duration of use, as well as the required PSI and CFM for your tools, should be a primary consideration when choosing an air compressor.
Infrequent vs. Continuous Use: Belt drive compressors are better suited for infrequent, intermittent use, while direct drive compressors excel in continuous, heavy-duty applications.
PSI and CFM Requirements: Ensure that the compressor you select can meet or exceed the pressure (PSI) and air flow (CFM) demands of your pneumatic tools for optimal performance.
Budget
Consider both the initial investment and the lifetime cost of the compressor when making your decision.
Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency plays a crucial role in the long-term operating costs of your air compressor.
Maintenance Capabilities
Your ability and willingness to perform maintenance tasks should be considered when choosing between belt drive and direct drive compressors.
Hands-on Maintenance vs. Professional Maintenance: Belt drive compressors require more frequent hands-on maintenance, such as belt tensioning and replacement, while direct drive models may need less frequent but more complex professional maintenance.
Environment
The environment in which the compressor will be operating can significantly impact its performance and longevity.
Harsh Conditions: Direct drive compressors are better suited for harsh environments with extreme temperatures, dust, or corrosive agents, as they have fewer moving parts and are more resilient to these conditions.
Noise Constraints: If the compressor will be used in a noise-sensitive area, belt drive models may be preferable, as they generally operate more quietly than direct drive compressors.
Flexibility
Consider your need for flexibility in terms of variable pressure and speed requirements.
| Factor |
Belt Drive |
Direct Drive |
| Usage Patterns |
Infrequent, intermittent use |
Continuous, heavy-duty use |
| Budget |
Lower initial cost, higher lifetime cost |
Higher initial cost, lower lifetime cost |
| Energy Efficiency |
Lower efficiency |
Higher efficiency, long-term savings |
| Maintenance |
More frequent, hands-on maintenance |
Less frequent, professional maintenance |
| Harsh Environments |
Less suitable, more susceptible to wear |
Better suited, more resilient |
| Noise Constraints |
Quieter operation |
Louder operation |
| Flexibility |
Greater adjustability with pulleys |
Limited adjustability |
Typical Applications for Each Compressor Type
Belt drive and direct drive air compressors are both widely used in various industries and applications. However, each type has its strengths and is better suited for certain situations. Understanding the typical applications for each compressor type can help you make an informed decision when choosing between a belt drive and direct drive air compressor.
Belt Drive Air Compressors
Belt drive air compressors are well-suited for a range of applications, particularly those requiring flexibility, lower noise levels, and intermittent use.
Workshops (Woodworking, Automotive Repairs): Belt drive compressors are a popular choice for woodworking and automotive repair shops. They offer the versatility needed for various pneumatic tools and tasks, such as sanding, painting, and powering impact wrenches.
Small to Medium-Scale Operations: Small businesses and medium-scale operations often benefit from the lower initial cost and adaptability of belt drive compressors. They can efficiently handle the demands of these settings without excessive investment.
Indoor Settings with Noise Constraints: In indoor environments where noise levels must be minimized, such as residential areas or office spaces, belt drive compressors are preferred. They operate more quietly than direct drive models, reducing the potential for noise disturbances.
Applications Requiring Pressure Adjustments: Belt drive compressors offer greater flexibility in adjusting pressure settings by changing pulley sizes. This makes them ideal for applications that require varying pressure levels for different tasks or tools.
Direct Drive Air Compressors
Direct drive air compressors excel in heavy-duty, continuous-use applications and harsh environments where reliability and efficiency are top priorities.
Industrial Applications (High CFM and Continuous Operation): Direct drive compressors are the go-to choice for industrial settings that demand high air flow (CFM) and continuous operation. They can withstand the rigors of these environments and deliver consistent performance.
Harsh Outdoor Environments: In outdoor settings with extreme temperatures, dust, or moisture, direct drive compressors are the better option. They have fewer moving parts and are more resilient to these harsh conditions, ensuring reliable operation and longevity.
Heavy-Duty Applications (e.g., Jackhammers, Construction): For heavy-duty applications like jackhammering and construction work, direct drive compressors are the preferred choice. They can handle the high demands and continuous use required in these industries.
Environments with Limited Space: Direct drive compressors have a more compact design due to the absence of belts and pulleys. This makes them suitable for environments with limited space, as they can be installed in tighter areas without compromising performance.
| Application |
Belt Drive |
Direct Drive |
| Workshops |
✓ |
|
| Small to Medium-Scale Operations |
✓ |
|
| Indoor Settings (Noise Constraints) |
✓ |
|
| Pressure Adjustments Required |
✓ |
|
| Industrial (High CFM, Continuous) |
|
✓ |
| Harsh Outdoor Environments |
|
✓ |
| Heavy-Duty Applications |
|
✓ |
| Limited Space Environments |
|
✓ |
By understanding the typical applications for belt drive and direct drive air compressors, you can select the type that best suits your specific needs, ensuring optimal performance and longevity for your pneumatic tools and operations.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance
Proper maintenance and timely troubleshooting are essential for ensuring the optimal performance and longevity of your air compressor, regardless of whether it is a belt drive or direct drive model. Each type has its own set of common issues and maintenance requirements that should be addressed to keep your compressor running smoothly.
Belt Drive Air Compressors
Common Issues
Belt Misalignment: Misaligned belts can cause uneven wear, reduced efficiency, and increased noise. Regularly check the alignment of the belts and adjust them as needed to ensure they run smoothly and evenly.
Belt Wear and Tension Problems: Over time, belts can stretch, fray, or crack, leading to reduced performance and potential breakage. Inspect the belts periodically for signs of wear and replace them when necessary. Ensure that the belts maintain proper tension to prevent slippage and minimize wear.
Maintenance Tips
Regular Lubrication: Belt drive compressors require regular lubrication to keep the moving parts running smoothly and minimize friction. Follow the manufacturer's guidelines for the recommended type and frequency of lubrication.
Periodic Belt Alignment and Replacement: Regularly check the alignment of the belts and adjust them as needed to ensure optimal performance. Replace worn or damaged belts promptly to avoid further issues and maintain efficiency.
Direct Drive Air Compressors
Common Issues
Shaft Seal Failures: The shaft seal, which prevents air and oil leaks between the compressor pump and the motor, can fail over time. This can lead to reduced performance, oil leaks, and potential damage to the compressor. Monitor the shaft seal for signs of wear and replace it when necessary.
High Repair Costs: Due to the direct connection between the motor and the compressor pump, repairs on direct drive compressors can be more complex and costly compared to belt drive models. Regular maintenance and prompt attention to any issues can help minimize the need for expensive repairs.
Maintenance Tips
Periodic Oil Changes: Direct drive compressors require regular oil changes to ensure proper lubrication and prevent contaminants from accumulating in the system. Follow the manufacturer's recommendations for oil type and change intervals.
Monitoring Wear on Critical Components: Regularly inspect critical components, such as the motor, compressor pump, and valves, for signs of wear or damage. Address any issues promptly to prevent further damage and maintain optimal performance.
| Compressor Type |
Common Issues |
Maintenance Tips |
| Belt Drive |
- Belt Misalignment |
- Regular Lubrication |
|
- Belt Wear and Tension |
- Periodic Belt Alignment and Replacement |
| Direct Drive |
- Shaft Seal Failures |
- Periodic Oil Changes |
|
- High Repair Costs |
- Monitoring Wear on Critical Components |
Conclusion
Belt drive and direct drive air compressors have distinct differences. Belt drive offers flexibility, quiet operation, and lower initial costs. Direct drive provides efficiency, durability, and low maintenance.
Choosing between them depends on your specific requirements. Consider factors like environment, usage patterns, budget, and maintenance capabilities.
Evaluating your needs carefully will lead to the best compressor choice. This ensures optimized performance and cost-effectiveness for your application.
Aivyter, a leading air compressor manufacturer, delivers top-quality products and exceptional service. With our experienced team and advanced technology, we provide reliable solutions for your compressed air needs. Choose Aivyter for optimized performance and cost-effectiveness. Contact us today to discuss your requirements and achieve full satisfaction.
English
العربية
Français
Русский
Español
Português
Deutsch
italiano
日本語
한국어
Nederlands
Tiếng Việt
ไทย
Polski
Türkçe
አማርኛ
ພາສາລາວ
ភាសាខ្មែរ
Bahasa Melayu
ဗမာစာ
தமிழ்
Filipino
Bahasa Indonesia
magyar
Română
Čeština
Монгол
қазақ
Српски
हिन्दी
فارسی
Kiswahili
Slovenčina
Slovenščina
Norsk
Svenska
українська
Ελληνικά
Suomi
Հայերեն
עברית
Dansk
اردو
Shqip
বাংলা
Hrvatski
Afrikaans
Gaeilge
Eesti keel
Māori
සිංහල
नेपाली
Oʻzbekcha
latviešu
অসমীয়া
Aymara
English
العربية
Français
Русский
Español
Português
Deutsch
italiano
日本語
한국어
Nederlands
Tiếng Việt
ไทย
Polski
Türkçe
አማርኛ
ພາສາລາວ
ភាសាខ្មែរ
Bahasa Melayu
ဗမာစာ
தமிழ்
Filipino
Bahasa Indonesia
magyar
Română
Čeština
Монгол
қазақ
Српски
हिन्दी
فارسی
Kiswahili
Slovenčina
Slovenščina
Norsk
Svenska
українська
Ελληνικά
Suomi
Հայերեն
עברית
Dansk
اردو
Shqip
বাংলা
Hrvatski
Afrikaans
Gaeilge
Eesti keel
Māori
සිංහල
नेपाली
Oʻzbekcha
latviešu
অসমীয়া
Aymara




















